Longread Guide: Types of Blockchain
No matter if you’re a crypto enthusiast or a trader, you have to know how the heart of any exchange works. We prepared a wholesome paper about the basics of blockchain for you to clarify all details you might not know before.
Read this long-read guide to find out what blockchain will suit your project the most or how your favorite token works, the difference between custom and off-the-shelf blockchain solutions, and what blockchains are available on the P2B exchange.
What is a blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger or database stored on the network nodes participating in the transaction validation. Initially, blockchain appeared as an innovative technology that lies in the basis of the cryptocurrency system while maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions.
The main benefit of this technology is providing transparency and high-level security in recording data and generating trust without a mediator. Do you want to find out how many types of blockchains have emerged after Bitcoin introduced blockchain to the world? Read this longread guide.
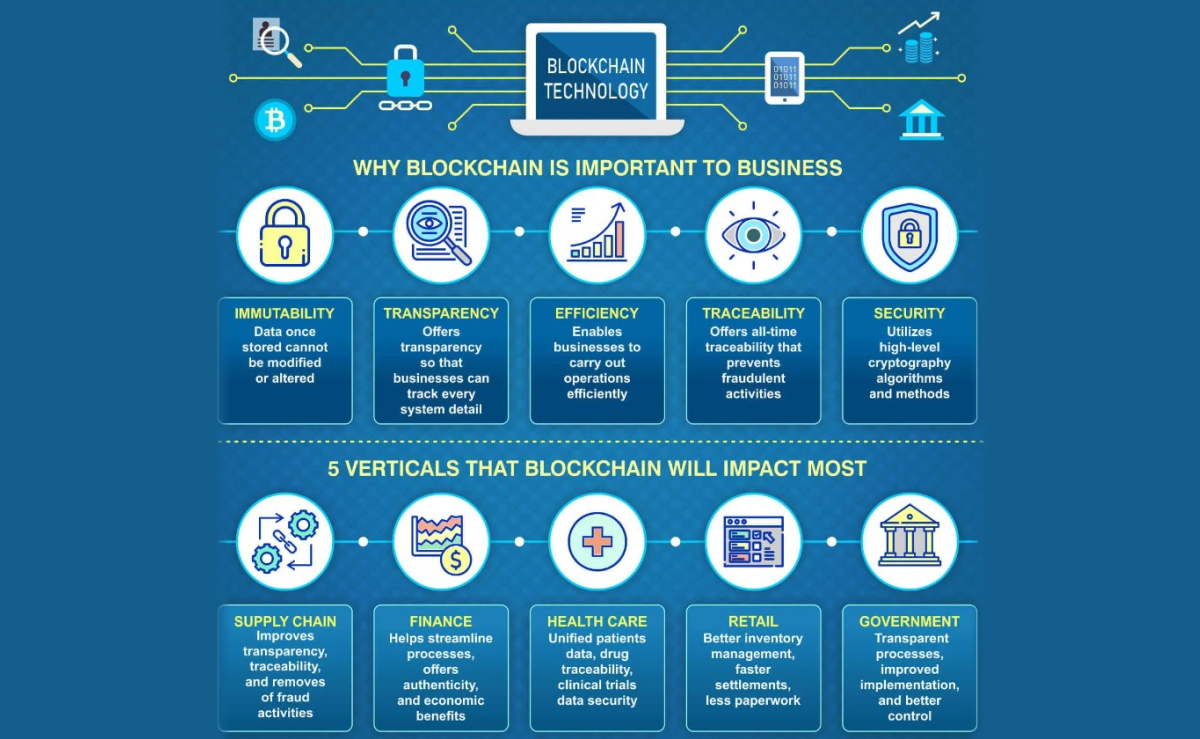
Blockchain is an innovative technology implemented in diverse fields of contemporary life. You can understand the blockchain’s importance while learning what types of problems to blockchain programmers solve.
Source: Investopedia
Immutability
Due to the way of storing information in the chain of the distributed ledger, blockchain is highly immutable. This feature caused blockchain to be one of the most popular technologies applied to the supply chain for transiting packages without hindrance.
Transparency
A public blockchain is transparent, which is very useful for different functions of contemporary society. Companies implement blockchain in their businesses to ensure end-users can interact with the processes fully or partially transparently.
Digital Freedom
Using blockchain, no centralized structure controls your financial operations. Unlike the bank, you can withdraw assets when you want and do it without authorization. It provides customers with digital freedom based on the background of blockchain technology.
Excellent Use Cases
It can be implemented in every field of our contemporary life, including trade finance, banking system, government, education, healthcare, real estate, and much more.
A high level of security
Due to its decentralized structure, blockchain can boast higher security than other systems. Cryptography uses complex mathematical algorithms to secure the data on the blockchain network. In addition, each block on the network carries a unique hash, meaning that data is not vulnerable to malicious attacks and can’t be hacked.
Affordability
Thanks to the decentralization of the newly-invented technology, the mediator does not need to process transactions. Therefore, the network participants don’t pay the mediator’s fees, which drops costs.
Enhanced Efficiency
Efficiency is also one of the main features of blockchain technology, making it more and more popular. Reasons for better efficiency include better security, intermediary removal, and overall better processes. A transaction in the blockchain takes several seconds rather than weeks to be processed.
Source: 101blockchains
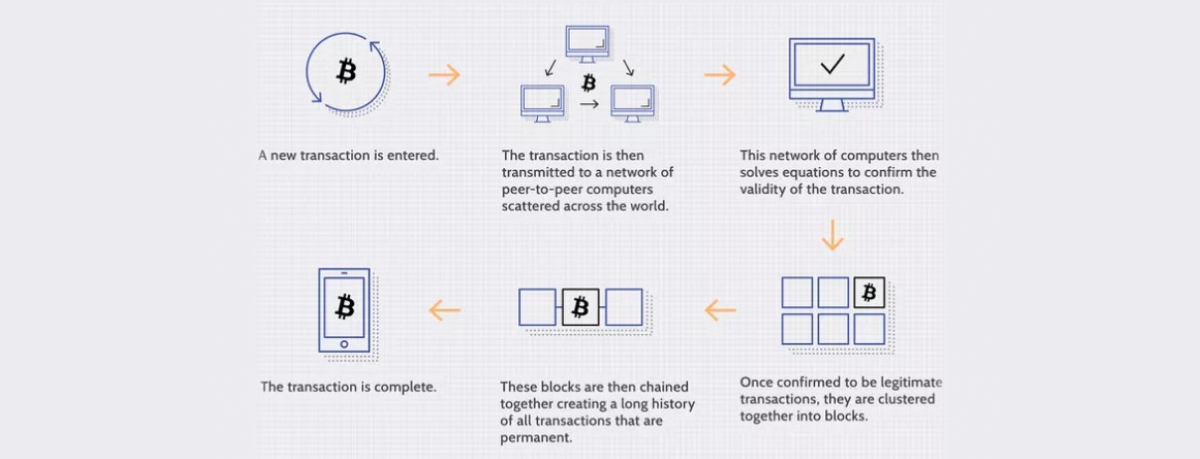
How blockchain works
In the blockchain network, data is collected in groups, known as blocks holding sets of information. All types of transactions can be stored in blocks on a blockchain. Certain storage capacities characterize blocks. Filled blocks are closed and linked to the previous block. These blocks together create a chain of blocks that is a blockchain. All the following data creates a new block that is also added to the chain of the blocks. The different types of ledger in blockchain include Blockchain itself, Hashgraph, DAG, Holochain, and Tempo (Radix).
The main aim of the blockchain is to record and distribute digital data, and it doesn’t allow it to be edited. All types of transactions can be stored in blockchain. Thus, a blockchain records transactions that can’t be altered, deleted, or destroyed.
This is how the blockchain works. However, let’s consider the history of the invention of the blockchain from scratch. In 2008, a white paper published by Satoshi Nakamoto introduced the concepts behind Bitcoin and blockchain. Nakamoto is a well-known pseudonym used for the crypto enthusiasts who developed the blockchain concept and can be considered the “founding fathers” of the blockchain. Blockchain supports secure, peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, including governments and banks. This was a real revolution in the collection and storage system of data.
The Bitcoin blockchain architecture invented by Satoshi Nakamoto was based on technologies and concepts from the previous three decades. Nacamoto’s design also introduced the “chain of blocks” concept. Satoshi Nakamoto defined a digital coin as a “chain of digital signatures” in which each owner transfers the coin to the next owner. The validation of the transaction includes signing a hash of the previous transaction and the next owner’s public key and adding them to the end of the chain.
Blockchain also lies in the basic of the Web, a catch-all term for the vision of a new, better Internet. The newly-invented version of the Internet uses blockchains, cryptocurrencies, and NFTs to provide network users with power in the form of ownership.
Web3 can boast several significant features:
- Decentralization. All the network participants, including builders and users, control the Internet instead of the centralized entities.
- Permissiolessness. Each member can participate in the network, and anybody isn’t excluded.
- Native payments. This network uses cryptocurrency for spending and sending online instead of depending on the outdated infrastructure of banks and payment systems.
- P2P system. At the network’s core, incentives and economic mechanisms are used instead of depending on the mediators.
Source: Investopedia
Why do we need different types of blockchain?
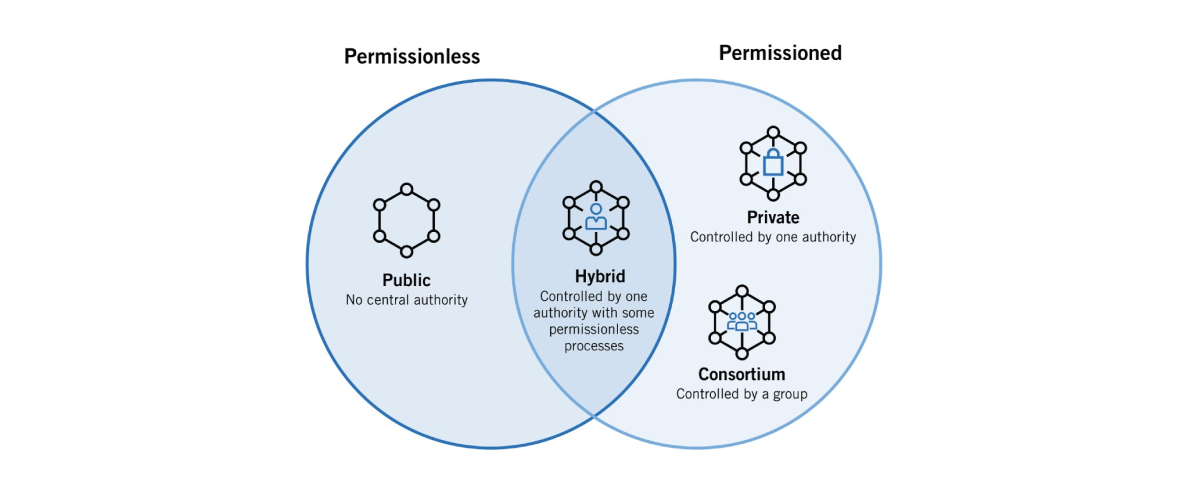
There are diverse types of blockchain because of the different purposes of their implementation. Followers often ask: “What are the 4 different types of blockchain technology?” There are four blockchain types: public, private, hybrid, and consortium. So, let’s consider different reasons for the invention of different types of blockchain:
- Processing transactions or data transfers across a secure network;
- The way people apply blockchain and distributed ledger technologies or networks;
- A public blockchain network contains multiple nodes worldwide where anybody can become a node and exchange BTC;
- The bank can use a private blockchain network. In this case, the network is password-protected, and providing access to the bank has been approved. As a result, only participants in the local network have access to the local network.
Given all these aspects, blockchain can be set up in diverse ways based on usage and requirements. Let’s consider different types of blockchain and their advantages and disadvantages.
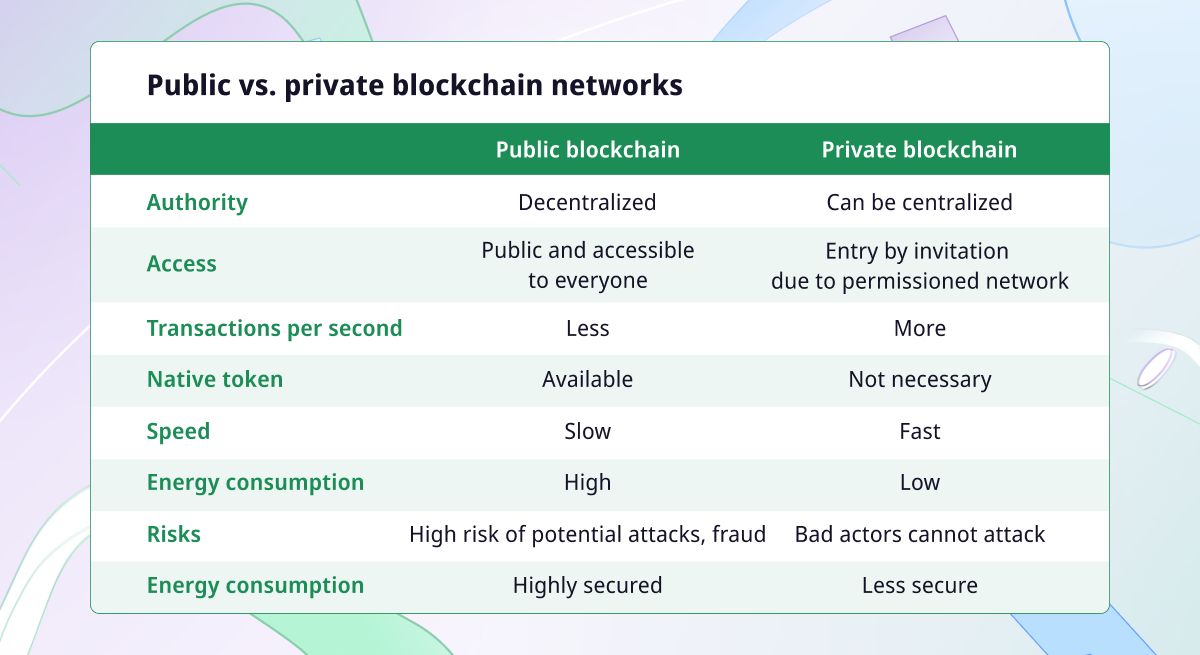
Public Blockchain
A public blockchain has the following characteristics:
- This is a permissionless distributed ledger where anybody can join and process transactions.
- This is a non-restrictive form of the ledger where each peer has its copy. A public blockchain is accessible to everybody with an Internet connection.
- Each user can access historical and contemporary records and perform mining operations. Miners perform complex computations to verify transactions and add them to the distributed ledger.
- In the blockchain, any valid record or transaction can’t be changed. The source code is open. Therefore, anybody can’t check transactions or suggest fixes.
Among the essential advantages of the public blockchain, we can emphasize the following:
- Trustworthiness. The proof-of-work consensus allows processing transactions without trust and protects the network from fraud.
- Security. The more the network is, the more records are distributed and the less probability of hacking the entire network.
- Transparency. All the member nodes have access to the public blockchain. Every authorized node contains a copy of the blockchain records.
Among the most significant disadvantages of a public blockchain, we can emphasize the following:
- Lower TPS. The number of transactions per second in a public network is lower than in a private one due to the huge number of nodes validating transactions in the network and completing a proof-of-work consensus algorithm.
- Scalability issues. The public blockchain has a lower speed for validating transactions, causing scalability issues. The more the network, the slower transactions are validated.
- High energy consumption. The proof-of-work consensus requires high energy consumption and needs to be improved.
Private blockchain
This type of blockchain is a restricted network or managed by a single identity. While having a similar peer-to-peer connection and decentralization to a public blockchain network, this network is far smaller. A private blockchain usually is set up on a small network within one organization or company. The private blockchain is a synonym for the permissioned blockchain.
The advantages are the following:
- Speed. In the private blockchain network, transactions are faster than in the public blockchain. The private blockchain contains fewer nodes which results in faster processing of transactions.
- Scalability. An owner can change the size of the private blockchain to meet specific requirements. This makes private blockchains particularly scalable since companies can increase or decrease the network size.
Check out the disadvantages private blockchain might have:
- Trust building. Fewer participants build a private network than a public blockchain.
- Lower security. The private blockchain contains fewer nodes which makes it more vulnerable.
- Centralization. Private networks are centralized since they require full administrative and monitoring capabilities provided by a central Identity and Access Management (IAM) system.
Source: Cointelegraph
Hybrid blockchain
This type of blockchain combines features of two other types of blockchain technologies, including private and public. Thanks to these features, companies can build a private, permission-based alongside a public, permissionless system. In addition, companies can decide who has access to blockchain data and what data can be public. In a hybrid blockchain network, transactions and records are typically private but can be validated through smart contracts.
Advantages of hybrid blockchain:
- High-level security. Hybrid blockchain provides a non-permitted environment protecting network members from a 51 percent attack.
- High cost-effectiveness. Due to the third-party contracts, transactions are cheap and fast while scaling better than public blockchain.
Disadvantages of hybrid blockchain:
- Non-transparency. Since data can be hidden, hybrid blockchain isn’t completely transparent.
- Less incentive. Since upgrades can be implemented with difficulty, users don’t have the incentive to become participants in the network.
Source: Foley
Consortium blockchain
Consortium blockchain also has features of private and public blockchains. This type of blockchain is also named a federated blockchain. This type of blockchain differs from the hybrid blockchain by involving different organizational members. In the consortium blockchain, predetermined nodes manage the consensus methods. The network contains a validator node that initiates, receives, and validates transactions. Member modes can initiate and receive transactions.
Among the most significant advantages of consortium blockchain, we can emphasize a high level of security. This type of network is more secure, scalable, and efficient than a public blockchain network. It also has access controls similar to private and mixed blockchains.
The most significant disadvantage of the consortium blockchain is a lack of transparency. If a member node is infiltrated, it can become a victim of a hacking attack. The network can stop working because of the blockchain’s rules.
Different types of nodes in the blockchain
There are diverse types of nodes in blockchain, including pruned full nodes, full nodes, archival full nodes, miner nodes, authority nodes, staking nodes, light nodes, masternodes, lightning nodes, and supernodes.
Pruned full nodes
Pruned full nodes store data on the hard disc. They have allocated storage space. Initially, such nodes download the entire blockchain to the hard drive and then remove older data block by block. They remove older blocks until the storage contains the most recent transactions.
Full node
Full nodes store blockchain transactions. PoW (Proof-of-Work) and PoS (Proof-of-Stake) consensus algorithms are based on validating transactions by the full nodes. Before the implementation of upgrades or improvements, the network ensures that full nodes are ready for this. These nodes participate in the management of the network.
Archival full node
Archival full nodes store and maintain the entire blockchain database. This is the most common type of blockchain node and doesn’t have a defined storage limit. Archival full nodes can be of different types, including authority, staking, miner, and master nodes.
Miner nodes
Miner nodes are types of blockchain nodes that operate on the Proof-of-Work consensus algorithm. Miner nodes need to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. A miner must have highly complex computing devices to solve these math problems. In addition, while solving math problems, these computing devices consume a lot of electricity. Miners get rewards for solving math problems and adding blocks of transactions to the chain.
Authority nodes
In a public blockchain, a node downloads and synchronizes blockchain data with the network. In private and some partially-centralized blockchains, authority nodes complete these tasks. They can manage and limit the access of the other nodes.
Staking nodes
Staking nodes validate transactions in the blockchains that operate on the Proof-of-Stake consensus algorithm. Network members lock a certain number of native tokens from that ecosystem on the blockchain to set up a staking node. A random staking node validates transactions and logs them on the ledger. This node is chosen by the network on some predefined rules. For instance, some networks consider the number of locked funds, while others consider the amount of time spent on the blockchain. Staking nodes use much less energy than miner nodes to process transactions.
Light Nodes
Light nodes are the second most popular type of blockchain node. The main purpose of the nodes is to accommodate faster transactions and daily activities. Also, they are called Simplified Payment Verification (SPV) nodes. They are developed to store only the block headers rather than downloading and storing the entire blockchain like full nodes. This results in a significant amount of time and storage space.
Masternodes
Masternodes are complete nodes that don’t add new blocks to the chain. They just validate and record transactions. This type of node can also perform any additional functions or responsibilities that are assigned to them. Masternodes were used for the first time in the Dash network in 2014.
Lightning nodes
If a blockchain network is overloaded, delayed transactions can appear in the network. Lightning nodes are applied to reduce transaction latency to a bare minimum. These nodes build a network where transactions are instantaneous and very cheap.
Supernodes
Supernodes belong to less popular types of node in blockchain. They intend to carry out specific tasks. A blockchain, for example, can use super nodes to maintain network regulations or to implement an upgrade.
How blockchain appears
There are different ways the blockchain appears. Hard forks, soft forks, and sidechains can appear in the network. When the split occurs in the network, this can be called a custom blockchain.
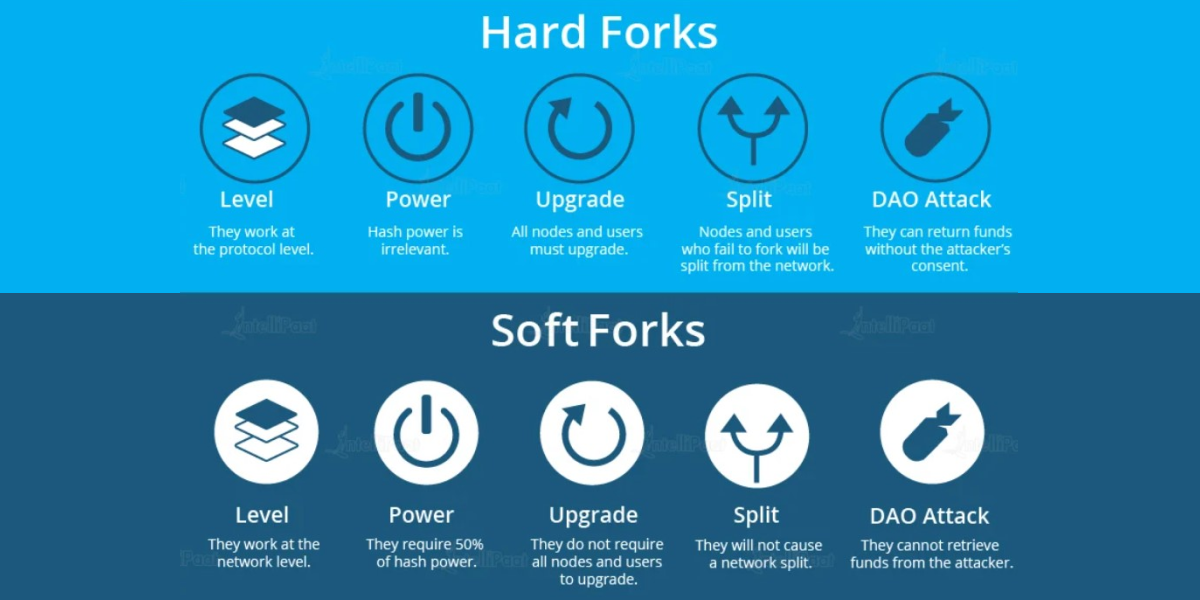
What are the two types of forks blockchain?
There are two types of blockchain forks: soft and hard. A fork occurs when a chain splits. Sometimes, for diverse reasons, a block has two different successive blocks that are not connected to each other. A fork in the chain starts from each of these two blocks that are not connected to each other.
Forks can be random. Sometimes, two miners mine two diverse blocks almost simultaneously while using the same protocol. In such cases, one of the two blocks is ignored, and another one is selected as the correct one.
Soft Forks
Soft forks don’t produce forks because they appear due to protocol updates that make the new blocks compatible with the previous protocol.
When a soft fork occurs in the network, blocks are mined or created using a new additional protocol. The network participants who want to continue using tools based on the old protocol can continue to do so. They just don’t have access to the new protocol’s new features.
In these cases, forks don’t occur in the blockchain, but they are still called forks since the protocol implemented in the new blocks’ work differed from the protocol implemented in the previous blocks’ work.
Hard fork
A hard fork occurs when the blocks produced with the new protocol are incompatible with the old one. Those participants who don’t want to use tools updated in the new protocol won’t be able to access the new blocks created with it. Regarding the hard fork, it appears when someone continues to mine or create blocks utilizing the old, outdated protocol. Since newly-created blocks are incompatible with the new protocol, two blockchains are created. The first one continues the previous one using the old protocol. And another one continues the previous one but with a new protocol.
For instance, it happened in 2016 to the Ethereum network. A new protocol appeared that was not compatible with the original 2015 protocol. The blockchain with the original protocol is Ethereum Classic (ETC), while the blockchain with the new protocol is Ethereum (ETH).
Source: Intellipaat
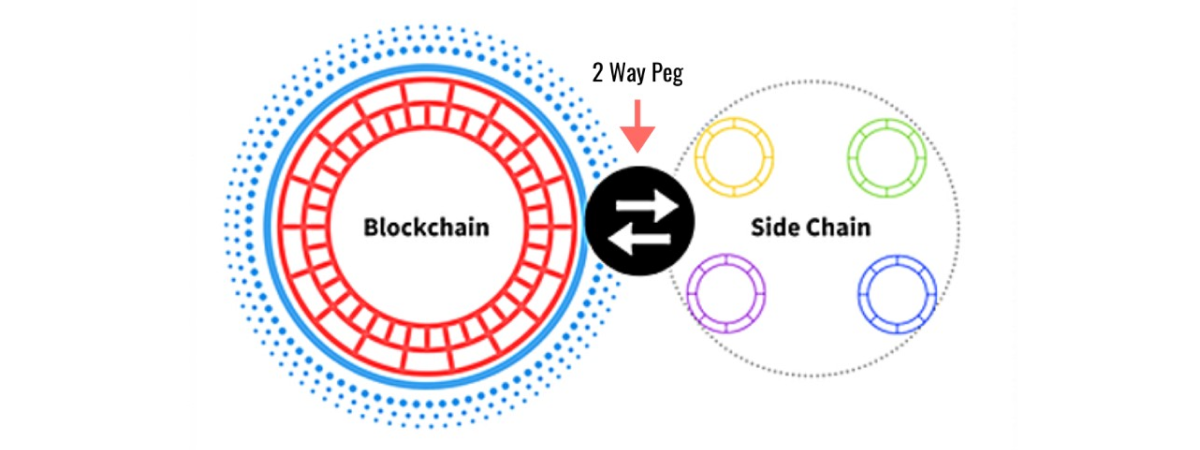
Sidechain
Sidechain is an independent blockchain that is connected to another main blockchain (the mainnet) via a two-way peg. In the network, tokens can be exchanged between the primary mainnet blockchain and the secondary sidechain in both directions. Sidechains are not forks of the blockchain but new blockchains that appear from the main blockchain at some point.
One of the most popular sidechains is Polygon which provides transactions in Ethereum tokens to be processed faster and at lower fees. Participants in the network can exchange Ethereum tokens for the corresponding tokens on Polygon immediately, without mediators and restrictions.
After the exchange, the new tokens can be used in the Polygon sidechain, which is faster and cheaper. In addition, they can be exchanged into the original tokens at any time. Polygon is based on the PoS (Proof-of-Stake) consensus protocol, while Polygon is based on the PoW (Proof-of-Work) consensus protocol.
When it comes to the Ethereum network, we can observe different types of blockchain appearance, including hard forks, soft forks, and sidechains.
Source: Blockchainfiles
Altcoins
When a group of networked peers continues to run a forked version of BTC with alternative consensus rules, a new alternative blockchain appears, and these peers effectively run a new cryptocurrency. This token is often called “altcoin.” For instance, well-known cases of altcoins forked from Bitcoin’s original code are Litecoin, Dogecoin, and Peercoin.
As an alternative option, a developer can create a new cryptocurrency while using elements of the prior cryptocurrency software or developing the code from scratch. If a developer designs a cryptocurrency from scratch, this is a custom blockchain. Cryptocurrencies designed from scratch are called altcoins. One of the most popular examples of altcoins created from scratch is Ethereum.
Metacoins
Sometimes, developers create a protocol built on top of the existing cryptocurrency to provide some specific consumer or enterprise service with the benefits of the blockchain.
For instance, the Counterparty system is built on top of Bitcoin’s blockchain. These second-layer systems use their own token XCP and allow users to issue new versions of scarce tokens for their particular purposes.
An individual can issue tickets to their concert and sell these tickets online as unique tokens on the Counterparty protocol, allowing owners of the tickets to resell them. At the concert, only those individuals who can poove that they are the final holders of ticket-tokens according to the records kept in the Bitcoin blockchain and interpreted by the Counterparty protocol have access to the performance. This can be performed without centralized companies, including Telecharge or Ticketmaster.
Tokens
Tokens resemble cryptocurrencies. They are types of currency based on blockchain and can be transferred from one account to another one. However, their behavior is not built into the blockchain software itself but is based on smart contracts. Most tokens are based on the EIP-20 token standard. All smart contracts are practically built on one standard while making them easy for users, wallets, and exchanges to interact with them.
To transfer tokens, an account signs a transaction notifying the smart contract to debit tokens and credit the same number of tokens to another account.
For instance, in the Ethereum network, Ether is the cryptocurrency; other “currencies” belong to tokens. On RSK, RBTC is a cryptocurrency, and other “currencies” are tokens.
Let’s consider the difference between tokens and cryptocurrencies:
- Fees (or gas) charged for processing transactions are cheaper when transferring cryptocurrency and more expensive when transferring tokens.
- Fees (or gas) are usually paid in cryptocurrency. Therefore, when transferring tokens, a user must have some cryptocurrency in their account.

Source: Blog.cryptostars
Custom blockchain solutions
Many companies implement custom blockchain solutions into their operations. However, off-the-shelf blockchain solutions don’t always fit the specific needs of a business. Learn why businesses may need custom blockchain solutions and the benefit they can get.
Benefits of the custom blockchain solutions:
- Unique Business Requirements. Custom blockchain solutions are tailored to the business’s unique needs, which increases the level of efficiency and productivity.
- Integration with Existing Systems. Developers can integrate custom blockchain solutions with their existing software.
- Scalability. Custom blockchain solutions can grow with the business, so they can expand their operations without the limitations of their blockchain solutions.
- Security. Custom blockchain solutions are developed to meet unique businesses’ requirements and provide them with high-level security protecting businesses from hacking attempts.
- Cost-effectiveness. Custom blockchain solutions can be cost-effective in the long-term perspective. While off-the-shelf blockchain solutions may be cheaper at the beginning of the project, custom blockchains are business-oriented and designed to meet specific requirements that can result in high-level efficiency and productivity in the long-term perspective.
The process of custom blockchain development
Custom blockchain solutions are widely implemented in diverse industries, including finance, healthcare, and logistics. However, pre-existing blockchain platforms don’t meet all the requirements of all businesses. Let’s consider all the stages of the development of the custom blockchain solutions:
- Defining the problem. The first stage of developing a custom blockchain is DApp (decentralized application) development. By designing dApp, you can improve supply chain transparency or build a secure platform for financial transactions. You need to understand the business’s specific needs to ensure the blockchain project completely meets the business’s requirements.
- Designing the architecture. After defining the problem, the next step is designing the blockchain solution architecture. This stage involves choosing the type of blockchain, whether it would be a public or private blockchain, the types of nodes, and which one of the types of consensus in a blockchain would be used. The architecture of blockchain should be scalable and secure.
- Developing smart contracts. These are self-executing contracts with terms that are directly written into the code. Smart contracts are components of blockchain technology and automate the execution of transactions. They are developed to meet the specific requirements of the business.
Different types of custom blockchain development
There are two different types of blockchain technology development. The first one is building a custom blockchain from scratch.
Benefits and risks of custom blockchain development from scratch
This way of blockchain development matches blockchain startups and fintech companies which want to enter the market with a unique product or service. A custom blockchain network is designed from scratch. Other architecture components are built on providing a required blockchain solution.
One of the main benefits of custom blockchain development is the possibility of implementing a blockchain solution completely tailored to specialized business needs. Another essential benefit of custom blockchain development is high-level security and the possibility to avoid vulnerabilities in the typical blockchain protocols, including Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, and so on. In addition, the unique mining and reward systems can be designed during the development of the custom blockchain.
Risks of custom blockchain development:
- Low-cost efficiency in the short-term perspective;
- Long-term development. Its development requires much time and high investments;
- Vulnerable network. New vulnerabilities can appear in the network;
- Low speed of processing transactions. Because of the lack of capacities, new blocks can be mined slowly, which results in a low speed of processing transactions.
Benefits and risks of forking a blockchain protocol
The second popular type of blockchain development is forking an existing blockchain protocol. This option is the best for companies that want to implement blockchain for corporate use.
In this case, a blockchain network is developed based on the open-source code of a well-established blockchain protocol, including Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, and others. The code is changed according to the requirements to provide a new blockchain network with different features and rules to work independently and host your blockchain apps.
The main benefits of forking a blockchain protocol:
- Cost-efficiency;
- 1.5-2 faster blockchain launch compared to custom blockchain development.
The main risks of forking a blockchain protocol:
- An untailored blockchain solution. One of the main risks is choosing an inappropriate blockchain protocol to fork.
- Low security caused by vulnerabilities in the network;
- Low scalability.
Blockchains supported on P2B
EOS
EOS is a blockchain platform allowing the development of industrial-scale decentralized apps. It can boast a solid underlying infrastructure to support this process.
The essential purpose of EOS is to provide user-friendly and business-friendly tools for developing decentralized applications. The platform overcomes the challenges of traditional platforms, including Ethereum.
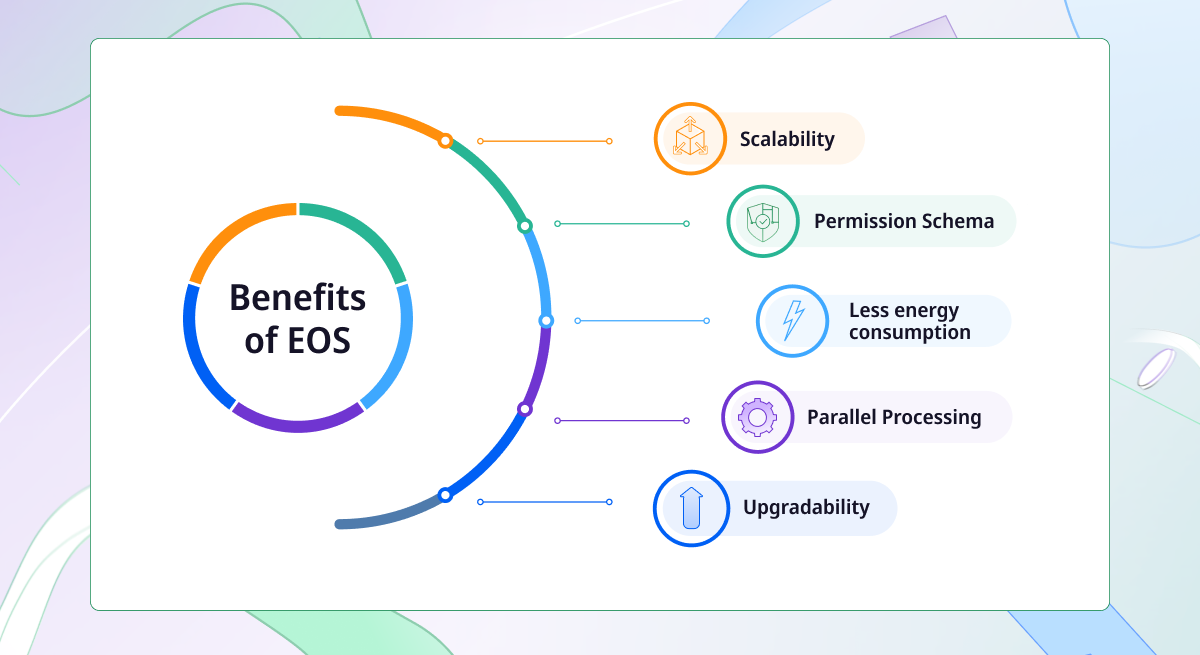
Let’s consider the main features of the EOS blockchain:
- High-level scalability. EOS allows the processing of millions of transactions in the network per second.
- Flexibility. EOS aims to provide security from vulnerabilities that are in the Ethereum network because of the DPOS (Delegated Proof-of-Stake) mechanism.
- Permission Schema. EOS offers a comprehensive permission system to create custom permission schemes for various business situations.
- Upgradability. DApps designed on the EOS blockchain platform are upgradeable. Users can go through the authorization to deploy code fix, add, or change features and even upgrade the application logic.
- Less energy consumption. EOS consumes less energy compared to others.
- Parallel Processing. In the network, parallel processing is available due to horizontal scalability, asynchronous communication, and interoperability.
- Decentralizied operating system. Ethereum is a decentralized supercomputer. EOS is a decentralized operating system enabling many business-friendly and user-friendly functions.
Source: Leewayhertz
Waves
Waves is a multi-purpose blockchain platform offering a gateway for Web3 technologies, including decentralized apps (dApps) and smart contracts. The blockchain platform is founded in 2016. The platform is popular for a wide assortment of products and services. It can boast its own programming language (Ride). In addition, it has a native crypto exchange offering many staking options.
Waves enables a developer-friendly infrastructure with a wide range of innovative tools. One of the main benefits of the platform is allowing users to design and launch custom crypto tokens without the need to build smart contract programming.
Source: 101blockchains
XRP
XRP is a fast, energy-efficient, and reliable decentralized public blockchain platform. Offering low transaction costs and a knowledgeable community, this is a strong open-course platform to develop projects. Among the essential benefits of the platform are the following:
- Open-source public and decentralized platform;
- Streamlined development. Tools that help speed up development and reduce the time to market;
- High-performance processing a thousand transactions per second;
- Low cost;
- High reliability. More than 63 million ledgers have been performed.

Source: Blockchain-council
Avalanche
Avalanche is a blockchain platform offering tools and features for the launch of DeFi decentralized apps. In addition, a platform allows for issuing financial assets, trading, and building enterprise-scale financial solutions. The system is based on the smart-contracts. This network enables customers and companies to issue their crypto assets and dApps for diverse use cases and public and private blockchain networks. The platform provides an interoperable ecosystem where users can interact with diverse networks and apps based on the platform.
One of the main benefits of the platform is high-level security. Two diverse protocols provide the network, including a modified version of the Proof-of-Stake and Snowman protocols. The last one secures C-chain and P-chain to contribute smart contract operations with fast responses. Snowman protocol is chain-optimized to secure smart contracts. At the same time, the entire network is provided by the architecture split across three diverse blockchains, including X-Chain, C-Chain, and P-Chain.

Source: Reddit
Polkadot
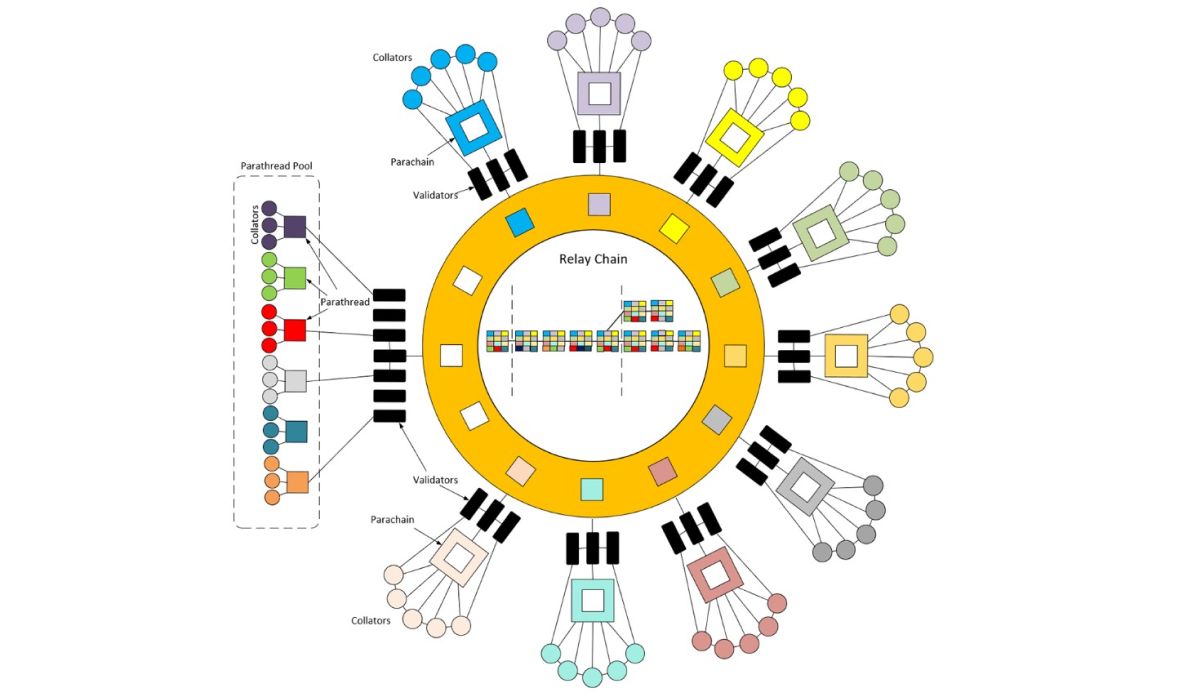
Polkadot is a new-generation blockchain promoting a heterogeneous multi-chain framework. The platform enables an ecosystem that tries to complete challenges that blockchain currently faces, including scalability and security.
Polcadot is one of the innovative types of blockchain platforms due to the set of its unique properties. This is a blockchain with a core network where other blockchains connect and communicate with each other. By hosting blockchain, the core chain also provides security and transactions, providing cross-chain interoperability.
The flexible and adaptive network architecture of Polcadot allows to build new networks on top. It provides different types of blockchain developers with the advantages of scalability, interoperability, and high-level security.
Source: Unblock
Algorand
Algorand is a decentralized and autonomous blockchain network offering many secure, efficient, and scalable apps. The innovative technology provides high-performance layer 1 blockchains that can boast security, scalability, privacy, and transaction finality. This a set of solutions modifying the fundamental protocol to make the system more scalable. A layer-1 blockchain is one of the types of sharded blockchain.
The layer-1 blockchain provides performance, interoperability, scaling, and layer-2 smart contracts, while layer-2 scaling solutions provide payment scalability and off-chain computing.
Source: Cointelegraph
Stellar
Stellar is a decentralized network with a blockchain updated every two to five seconds. The consensus protocol of the Stellar network doesn’t depend on the entire miner network to validate transactions. Stellar is based on the Federated Byzantine Agreement (FBA) algorithm, which allows faster processing of transactions.
Each node in the network selects another set of “trustworthy” nodes. When the group of nodes validates a transaction, it’s considered approved. This mechanism provides the network with additional speed and enables the processing of 1000 network operations per second.
Source: blockchain.oodles.io
Cardano
Cardano is a Proof-of-Stake blockchain network. It’s well-known as a “third-generation” blockchain. Cardano intends to complete the scalability challenges that most “second-generation” blockchains face, including Ethereum.
Compared to the “second-generation” networks, Cardano is developed to ensure a truly decentralized, low-fee, high-TPS Proof-of-Stake (PoS) network solution.
The platform aims to fasten its network’s speed and overall capability in multiple ways. It’s based on the Ouroboros protocol, a modified version of the Proof-of-Stake consensus protocol. Ouroboros decreases the energy cost of the network, especially when compared to diverse types of blockchain PoW protocols, without harming the scalability.
Source: Cointelegraph
Terra
Terra is an open-source blockchain payment platform for an algorithmic stablecoin. The network allows users to spend, save, trade, or exchange Terra stablecoins instantly.
The protocol of the Terra platform designs stablecoins to track the price of a fiat currency. The network offers two tokens—Terra and Luna.

Source: cnbctv18
Fantom
Fantom is a DAG-based (Directed Acyclic Graph) smart contract platform allowing to design of decentralized apps (dApps). DAG is a data modeling and structuring technology. Its networks contain vertices and edges, unlike blockchains which are built on blocks. In these networks, crypto transactions are represented by vertices stacked on top of one another.
The network is based on the PoS protocol that is used to protect the network. The transaction’s processing time is around 1-2 seconds to complete.
The Fantom Opera mainnet is Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)-compatible and provides full smart contract functionality via Solidity. Thanks to high-level scalability, every app gets its independent blockchain with unique tokens, governance rules, and tokenomics.
Source: Cointelegraph
Metis
Metis is a Layer-2 roll-up platform based on Ethereum, offering low gas fees, fast transactions, native storage, and high-level security. Metis intends to complete the challenges that Ethereum has faced. Its mission is to build an accessible, easy-to-use technical platform allowing everybody to launch their business project, dApp, or community with scalability.
It’s compatible with Ethereum Layer 1. The platform applies Optimism rollups enabling developers to integrate fastly, cheaply, and easily.
Source: metisdao.medium
Polygon
Polygon has been designed to solve some problems of the Ethereum network. It supports more than 7000 dApps. Polygon is based on the Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism, rewarding token holders to maintain the network running and verify transactions.
Polygon applies various technologies to build this fast parallel blockchain and link it to Ethereum. The network has its native token Metis. The token enables paying transaction fees on the Metis network and staking for Decentralized Autonomous Companies (DACs) that validate transactions and send them to the Ethereum mainnet.

Source: Cointelegraph
Pivx
Pivx is an open-source cryptocurrency having the following features:
- SHIELD, a zk-SNARKs-based privacy protocol, provides security.
- Thanks to the Proof-of-Stake protocol, the environmental footprint is low, and network participation is equal.
- Decentralized Governance System. It’s based on top of the two Masternodes network providing a monthly community treasury, proposals submission, and decentralized voting.
- A high speed of transactions. The network offers a new and better instant transactions mechanism thanks to fast block times and the tier-two network.
- Easy-to-use. The network can boast an attractive possible graphical interface for a core node/wallet.

Source: Ambcrypto
Tron
Tron is a blockchain-decentralized digital platform with its own cryptocurrency. The network can validate 2000 transactions per second. It’s built on the Proof-of-Stake consensus. Network participants choose “super representatives” (SRs) to process transactions getting fees for their services.
The platform is created to help developers design DApps and smart contacts without charging high transaction fees and latency of conventional networks. To ensure all these benefits, the blockchain has a three-layer architecture with a core, storage, and application layer. Thanks to the Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) protocol algorithm, one individual manages only one node in the network.

Source: Outlookindia
Cross-chain
Cross-chain bridge is a software application enabling transactions to be transmitted between different blockchains. Cross-chain bridge plays an important role, while cryptocurrencies or tokens are transferred between blockchains. Cross-chain bridges provide inter-network transactions providing a much broader digital ecosystem. Thanks to the benefits of cross-chain bridges, cryptocurrency owners can expand the value of their crypto projects for a wider range of real-life uses.
Cross-chain bridges allow implementing of a lot of innovative processes. However, their security can suffer since these apps have experienced hacking losses. According to the technical aspects of cross-chain bridges, it’s best to apply them only if you understand how they work. In this case, you won’t face unexpected crypto losses.

Source: Academy.binance
Solana
Solana is a blockchain platform allowing to develop decentralized, scalable apps. The network enables processing much faster and charges lower transaction fees than Ethereum. Solana is much faster regarding the number of transactions it can process and has significantly lower transaction fees than rival blockchains like Ethereum.
In addition, Solana is a blockchain network based on the proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, which uses hashed timestamps to verify when transactions occur.

Source: Forbes
ERC-20
If you want to find out what are the different types of tokens in blockchain, read this paragraph. There are two types of tokens: NFTs (non-fungible tokens) and fungible tokens. A fungible token is interchangeable with another token, while NFTs are not interchangeable.
ERC-20 is the standard used for the developemnt of the fungible tokens designed on the Ethereum platform. ERC-20 allows developers to build smart-contract-enabled tokens which can be applied to other products and services. Fungible tokens represent an asset, ownership, access, cryptocurrency, or something else that is not unique but can be transferred.
Thanks to the ERC-20 implementation, most tokens have been created in the Ethereum ecosystem.
BSC
BSC is a blockchain network launched by the Binance exchange. It allows building smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). The network runs alongside the BNB Chain, previously Binance Chain. BSC supports smart contracts, while the BNB Chain allows high transaction volume with 3 seconds block time. Two blockchains together create Binance Chain.
BNB Smart Chain supports BNB, the native cryptocurrency of BNB Beacon Chain and BEP20 tokens. The blockchain runs on the proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus. Users can stake BNB to become validators who get transaction fees as a reward for the validation of each block.
BSC is compatible with Ethereum smart contracts and enables users to build DApps or even transfer them from Ethereum. BSC offers many DApps and DeFi (decentralized finance) products. The network supports decentralized exchanges, including PancakeSwap or BurgerSwap. Decentralized exchanges enable to trade or exchange tokens. Moreover, users can participate in lending, gaming, or yield farming on the decentralized exchanges.

Source: Bnbchain
How to choose a blockchain for a future crypto project depending on blockchain features
While choosing a blockchain for a future crypto project, pay attention to the following features:
- The level of security. Pay attention to the blockchain’s security level and mechanisms solving the vulnerabilities issues and protecting it from hacking attacks.
- Scalability. If the blockchain network has low scalability, this can cause a low speed of validating transactions in the future. Therefore, choosing platforms that have solved the scalability issues is better.
- Cost-efficiency of the crypto project. Building a custom blockchain will take more time but will match your expectations more. Using an existing blockchain platform will save time and will allow launching your crypto project faster.
- Types of decentralization in blockchain provided by the consensus algorithm. Blockchains built on the PoW (Proof-of-work) consensus require high computing power and consume a lot of energy while making a harmful environmental footprint. In such networks, the authority belongs to the miners. Blockchains based on the PoS (Proof-of-stake) consensus work according to other principles, where each participant in the network is a staker of the network and controls its node.
- Compatibility of the blockchain with the needs of your crypto project. Custom blockchain will better meet your crypto project’s needs than off-the-shelf blockchain solutions.
- The success of the platform to design a crypto project. Check on how many projects have been launched on this platform successfully.
- The speed of the crypto project development. If you choose a platform for your future crypto project development, it takes less time than developing a custom blockchain. However, developing a custom blockchain can be more cost-efficient in the long-term perspective.
Benefits of listing your token on the P2B exchange
Among the essential benefits of listing a token of the P2B exchange, we can emphasize the following features:
- High-level security. P2B is one of the most reliable crypto exchanges worldwide. According to the Сer.live rating, one of the most reliable independent crypto rating sources, the P2B security rating is AA, with an 88.30% security score.
- A wide variety of supported blockchains. The P2B exchange offers its customers various blockchains listed above. Therefore, you can choose the most suitable for your crypto project, matching your business’s needs.
- High-level reputation and experience in the crypto market. The P2B exchange has established itself as one of the most reputable crypto exchanges while taking top places in diverse ratings, including Coingecko, CryptoLists.com, Cryptowisser, Coincodex, Cryptocompare, Nomics, and others.
- Promotion and PR. Thanks to the cooperation with top-notch liquidity services, including PromoJ and LiquidLines, the P2B exchange offers its customers full-cycle support. It supports crypto projects at the beginning of their launch, starting from the crypto listing consulting and ending with crypto project marketing and promotion services. This allows launching your crypto project successfully while also promoting it among the target audience.
- Untouchable funds. Assets invested in the crypto project are stored in the customers’ wallets and are not used for the needs of the cryptocurrency exchange.
- Liquidity and volume. The P2B exchange can boast high-level liquidity, providing crypto projects with a high volume of trades and stabilizing prices.

Source: Token Variety on P2B Exchange



